This short articles explains what is biocatalysis, its mportance and how it can be used for the benefit of mankind and the environment.
The objective of this brief article is to make the reader aware of the importance of biocatalysis and how it can be used for the benefit of mankind and the environment. Biocatalysis refers to the use of biological agents, be it enzymes or living organisms to catalyse chemical reactions. The enzymes utilized can be in an isolated form or expressed within the living organism when the organism is used for catalyzing such a reaction. The advantage of using enzymes and living organisms is that they are very specific and do not yield unrelated products that is observed when using chemicals to carry out such reactions. Another advantage is that enzymes and living organisms work at less harsher conditions and are ecofriendly as opposed to chemicals being used for such transformations.
The process of catalyzing the reaction using enzymes and living organisms is known as biotransformation. Such biotransformation reactions not only occur in vivo within the human body (liver being the preferred organ; where cytochrome P450s are used to convert xenobiotics to water soluble compounds that can be excreted from the body), but also can be utilized ex vivo using microbial enzymes to perform reactions that are beneficial for mankind.
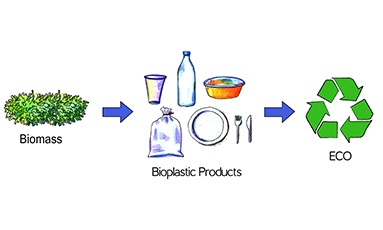
A plethora of avenues exist where biocatalysis1 and biotransformation reactions can be used for human and environmental benefit. One such area which warrants the use of such a technology is the production of plastic material, be it for manufacturing bags, cans, bottles or any such container (s), as chemically made plastics pose a huge threat to the environmental biodiversity and are non-biodegradable. They accumulate in the environment and are not able to get rid of easily. The use of enzymes and living organisms to produce bioplastics, plastics that can be easily biodegradable and pose no threat to environment would go a long way in not only reducing the chemically derived plastic waste but also help in sustaining ecosystems and prevent our flora and fauna from becoming extinct. The biodegradable containers made of bioplastic material would find use in several industries such as agri industry, food packaging, beverages and pharmaceuticals.
A variety of technologies exist today to produce bioplastics2-4. Some have been validated in the laboratory while others are still in the stage of infancy. Researches globally are working on such technologies to make them cost-effective5 and scalable so that they can be taken up to produce bioplastics in an industrial setting. These bioplastics can ultimately substitute chemically made plastics.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.29198/scieu1901
***
Source(s)
1. Pedersen JN et al. 2019. Genetic and chemical approaches for surface charge engineering of enzymes and their applicability in biocatalysis: A review. Biotechnol Bioeng. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.26979
2. Fai Tsang Y et al. 2019. Production of bioplastic through food waste valorization. Environment International. 127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.03.076
3. Costa SS et al. 2019. Microalgae as source of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) – A review. Int J Biol Macromol. 131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.099
4. Johnston B et al. 2018. The Microbial Production of Polyhydroxyalkanoates from Waste Polystyrene Fragments Attained Using Oxidative Degradation. Polymers (Basel). 10(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10090957
5. Poulopoulou N et al. 2019. Exploring Next-Generation Engineering Bioplastics: Poly(alkylene furanoate)/Poly(alkylene terephthalate) (PAF/PAT) Blends. Polymers (Basel). 11(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030556
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Rajeev Soni PhD (Cambridge)

Dr Rajeev Soni holds a PhD in Molecular Biology from University of Cambridge where he was Cambridge Nehru and Schlumberger scholar. He is an experienced biotech professional and has held several senior roles in academia and industry.
The views and opinions expressed in blogs are solely those of the author(s) and other contributor(s), if any.