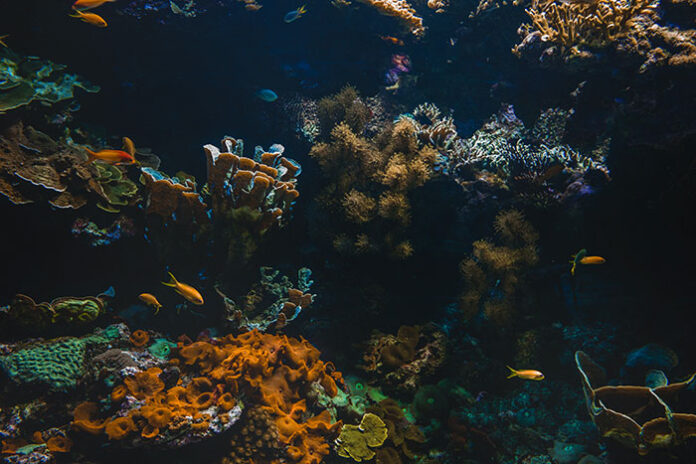
Hidden, oceanic internal waves have been found to play a role in deep-sea biodiversity. In contrast to the surface waves, the internal waves are formed as a result of thermal contraction in layers of the water column and help bring in planktons to the bottom of seabed thereby supporting benthonic animals. The study in Whittard Canyon showed that local hydrodynamic pattern associated with internal waves was linked to increased biodiversity.
Organisms living in the aquatic environment are either plankton or nekton or benthos based on their location in the ecosystem. Planktons could be either plants (phytoplankton) or animals (zooplankton) and usually swim (not faster than the currents) or float around in the water column. Planktons could be microscopic or larger ones like floating weeds and jellyfish. Nektons such as fish, squids or mammals, on the other hand, swim freely faster than the currents. Benthos like corals cannot swim, and usually live on bottom or seafloor attached or freely moving. Animals like flatfish, octopus, sawfish, rays mostly live on the bottom but can also swim around hence called nektobenthos.
The marine animals, coral polyps are benthos living on floor of seabed. They are invertebrates belonging to the phylum Cnidaria. Attached to the surface, they secrete calcium carbonate to form a hard skeleton which eventually take the form of large structures called corals reefs. Tropical or surface water corals commonly live in shallow tropical waters where sunlight is available. They require presence of algae that grow inside of them providing them with oxygen and other things. Unlike them, deep-water corals (also known as cold-water corals) are found in deeper, darker parts of the oceans ranging from near the surface to the abyss, beyond 2,000 metres where water temperatures may be as cold as 4 °C. These do not require algae to survive.
Oceanic waves are of two types – surface waves (at the interface of water and air) and internal waves (at the interface between two water layers of different density in the interior). The internal waves are seen when the water body consists of layers of different densities due to either differences in temperature or salinity. In the ocean ecosystem, the internal waves deliver food particle nutrients to surface waters that stimulate the growth of phytoplankton, and also contribute in transportation of food particles to deep sea animals.
Physical oceanography obviously has bearing on faunal patterns in deep sea biodiversity. In this study, the researchers integrated physical oceanography datasets with acoustic and biological datasets to do predictions, rather than using proxies for environmental variables, of distribution of deep-water corals and megafaunal diversity in Whittard Canyon, North-East Atlantic. The idea was to look for the environmental variables that best predict faunal patterns in canyons. They also wanted to know if incorporation of oceanographic data improved model’s ability to predict faunal distributions. It was found that local hydrodynamic patterns associated with internal waves was linked to increased biodiversity. Furthermore, performance of the prediction model improved with the inclusion of oceanographic data.
This research enables better understanding of the faunal pattern formation in deep water ecosystem which will be helpful in better conservation efforts and ecosystem management.
***
Sources:
1. National Oceanography Centre 2020. News – Deep-sea biodiversity and coral reefs influenced by ‘hidden’ waves within the ocean. Posted 14 May2020. Available online at https://noc.ac.uk/news/deep-sea-biodiversity-coral-reefs-influenced-hidden-waves-within-ocean Accessed on 15 May 2020.
2. Pearman TRR., Robert K., et al 2020. Improving the predictive capability of benthic species distribution models by incorporating oceanographic data – Towards holistic ecological modelling of a submarine canyon. Progress in Oceanography Volume 184, May 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pocean.2020.102338
3. ESA Earth Online 2000 -2020. Oceanic Internal Waves. Available online at https://earth.esa.int/web/guest/missions/esa-operational-eo-missions/ers/instruments/sar/applications/tropical/-/asset_publisher/tZ7pAG6SCnM8/content/oceanic-internal-waves Accessed on 15 May 2020.
***