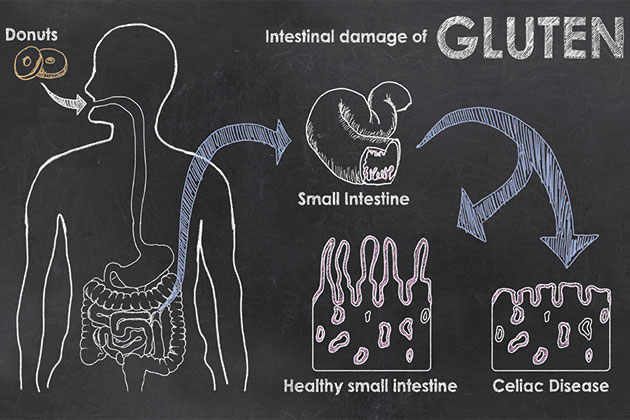
Study suggests a new protein involved in development of gluten intolerance which can be a therapeutic target.
Almost 1 out of 100 people suffer from celiac disease, a common genetic disorder which could sometimes also be triggered by environmental factors and diet. People suffering from celiac disease develop a sensitivity to gluten – found in wheat, rye and barley. This disease is a severe autoimmune disorder of our intestine in which our immune system triggers a response against our body’s own cells – hence the ‘autoimmunity’ – when any food containing gluten is consumed. This negative response by our immune system damages the surface of small intestine. Initially celiac disease was found in countries with higher Caucasian population, now its also being reported in populations. There is unfortunately no cure available for celiac disease and patients’ need to keep a strict watch on their diet which is the only therapy available.
Association between celiac disease and cystic fibrosis
Celiac disease also occurs higher (by almost three times) in people who suffer from cystic fibrosis as there is a definite co-occurrence between these two diseases. In cystic fibrosis, thick and sticky mucus builds up in the lungs and intestine mainly caused by mutations in the gene for protein CFTR (cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator). CFTR protein plays a central role in keeping the mucus fluidic. So, when this ion transport protein is not generated, mucus starts to clog up and this malfunction also triggers other problematic reactions in the lungs, intestines and other organs mainly due to the immune system getting activated. These reactions or effects are very similar to what is triggered by gluten in celiac disease patients. That is why it is being understood that these two disorders are linked.
Researchers from Italy and France set out to understand the nature of connection between celiac disease and cystic fibrosis at the molecular level in their study published in The EMBO Journal. Since gluten is very difficult to digest, its longer protein parts enter the intestine. Researchers used human intestinal cell lines in the laboratory which are sensitive to gluten. It was seen that one particular protein part (or peptide) called P31-43 is able to directly bind to CFTR and impair its function. And once function of CFTR is hindered, cellular stress and inflammation gets triggered. Researchers concluded that CFTR is crucial in mediating gluten sensitivity in celiac patients.
One particular compound called VX-770 could inhibit the interaction between the peptide P31-43 and CFTR protein by blocking the active site on the target protein. So, when human intestinal cells or tissues which were collected from celiac patients were pre-incubated with VX-770, the interaction between the added peptide and the protein did not take place and thus immune reaction was not elicited at all. This marks VX-770 as essential for protecting gluten-sensitive epithelial cells from the bad effects of gluten consumption. In gluten sensitive mice, VX-771 provides protection from gluten-induced intestinal symptoms.
This study is a promising first step towards developing a treatment via inhibitors of protein CFTR which can treat cystic fibrosis and may also be a starting point for developing a potential treatment for celiac disease. More clinical trials are needed to analyze the dose and administration of the potential CFTR inhibitors. Results could help patients who have gluten intolerance to be able to use medication without changing or restricting their diet.
***
{You may read the original research paper by clicking the DOI link given below in the list of cited source(s)}
Source(s)
Villella VR et al. 2018. A pathogenic role for cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in celiac disease. The EMBO Journal. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2018100101